Most Realistic War Strategy Game A Deep Dive
Most Realistic War Strategy Game? Oh boy, buckle up, buttercup, because this ain’t your grandma’s Candy Land. We’re diving headfirst into a world of meticulously crafted battlefields, cunning AI opponents, and enough strategic depth to make your head spin. Forget dice rolls; we’re talking about the kind of realism that’ll make you question if you’re playing a game or commanding a real army (don’t worry, no actual casualties involved…probably).
We’ll be dissecting the very essence of “realistic” in war strategy games, examining everything from historically accurate unit rosters and realistically modeled terrain to the often-frustrating, yet strangely satisfying, dance between AI opponents and human players. Get ready to explore the fine line between historical accuracy and engaging gameplay – because let’s face it, a perfectly realistic game that’s also utterly boring is about as useful as a chocolate teapot.
Defining “Realistic” in War Strategy Games
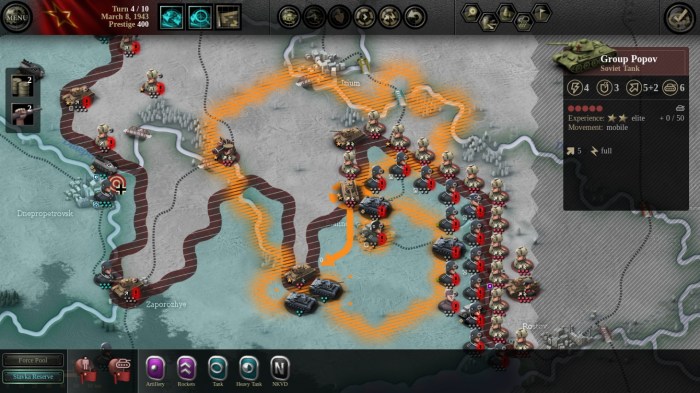
The pursuit of realism in war strategy games is a fascinating balancing act. It’s a constant negotiation between the desire to accurately reflect the complexities of real-world warfare and the need to create an engaging and playable experience. True realism, in the strictest sense, is often unattainable within the confines of a game, yet the striving for it shapes the design and player experience profoundly.The perceived realism of a war strategy game hinges on several key factors.
These factors interact in complex ways, making the creation of a truly “realistic” game a multifaceted challenge. The most significant aspects include the accuracy of unit statistics and capabilities, the simulation of terrain and its impact on combat, the modeling of logistical constraints, the representation of strategic decision-making processes, and the inclusion of unpredictable events that mirror the chaos of real warfare.
Key Factors Contributing to Realism
The level of detail in unit statistics significantly impacts realism. For example, accurately reflecting the strengths and weaknesses of different unit types – from the firepower of tanks to the mobility of infantry – is crucial. Similarly, the simulation of terrain, including elevation, cover, and weather conditions, directly affects unit movement and combat effectiveness. Logistical considerations, such as supply lines and resource management, add another layer of realism.
A game that accurately depicts the challenges of maintaining a large army far from its supply bases will feel more authentic than one that ignores these aspects. Finally, the inclusion of random events, such as unexpected enemy movements or equipment malfunctions, can inject an element of unpredictability that better reflects the chaotic nature of real warfare.
Game Mechanics: Enhancing and Detracting from Realism
Certain game mechanics enhance realism while others detract from it. Realism is enhanced by mechanics that accurately model the fog of war, forcing players to make decisions based on incomplete information. Similarly, realistic attrition models, where units suffer casualties and require replacement, add to the sense of immersion. Conversely, mechanics that allow for unlimited unit production or instant reinforcements can undermine realism by simplifying a crucial aspect of warfare.
Similarly, overly simplistic combat resolution systems, where the outcome is determined solely by numerical superiority, fail to capture the tactical nuances of real combat. The use of simplified unit types, neglecting the specifics of individual weapon systems or unit composition, also detracts from realism.
Comparative Analysis of Game Design Choices
Comparing different game design choices highlights the tension between realism and playability. Games likeHearts of Iron IV*, known for their intricate unit management and supply systems, prioritize realism over ease of play. In contrast, games like
Civilization VI* prioritize strategic depth and broad strokes over granular detail, sacrificing some realism for accessibility. This difference reflects a fundamental design choice
whether to prioritize a deeply immersive but potentially complex experience or a more streamlined and accessible one.
Total War
Warhammer*, on the other hand, uses a fantasy setting to explore similar strategic concepts but departs from historical accuracy to create a unique and engaging experience. This illustrates how the definition of “realistic” can shift depending on the game’s intended audience and setting.
Historical Accuracy versus Gameplay Balance
The conflict between historical accuracy and gameplay balance is a recurring theme in war strategy game development. Strict adherence to historical facts can sometimes lead to unbalanced gameplay, where certain nations or strategies are overwhelmingly dominant. Conversely, prioritizing gameplay balance might require altering historical facts, leading to a less historically accurate but more engaging game. For example, a game might adjust unit statistics to ensure a more competitive experience, even if this deviates from historical performance data.
This balancing act necessitates careful consideration and often requires compromises. The most successful games often find a delicate equilibrium between these two competing goals.
AI and Player Interaction
The heart of any compelling war strategy game lies in the dynamic interplay between the player and the artificial intelligence controlling opposing forces. A truly realistic experience hinges on the AI’s ability to mirror the strategic thinking and adaptive behavior of a human opponent, creating a challenging and engaging battle of wits. The sophistication of this interaction directly impacts the overall immersion and replayability of the game.The quality of AI in war strategy games varies considerably.
Consider the differences between, say, the relatively simplistic AI of older titles and the more sophisticated systems found in modern games. Older games often relied on pre-programmed responses and predictable patterns, leading to easily exploitable weaknesses. Modern games, however, leverage advanced algorithms, machine learning, and sometimes even neural networks to create more nuanced and adaptive opponents. This results in AI that can learn from past encounters, adjust its strategies, and even exhibit unexpected behaviors, making each playthrough unique and demanding.
Comparison of AI Opponents in War Strategy Games
Different war strategy games showcase varying levels of AI sophistication. Games likeHearts of Iron IV* boast AI capable of complex logistical planning and dynamic responses to shifting geopolitical situations, while others might focus on simpler mechanics, leading to more predictable AI behaviors. The strategic depth of the AI is directly proportional to the complexity of the game mechanics themselves; a game with intricate economic and technological systems will require a more advanced AI to manage those elements effectively.
Adaptive capabilities, on the other hand, often depend on the implementation of machine learning techniques, allowing the AI to learn from player actions and adjust its strategies accordingly. For example, an AI that consistently loses to a particular player strategy might adapt by focusing on countermeasures in subsequent games.
Factors Influencing the Realism of Player versus AI Interactions
Several crucial factors contribute to the realism of player versus AI interactions. These include the AI’s ability to convincingly simulate human decision-making processes, its capacity for strategic planning and adaptation, and its proficiency in managing resources and logistics. Additionally, the AI’s understanding and response to the game’s dynamic elements, such as terrain, weather, and unexpected events, significantly influence the realism of the experience.
A high level of unpredictability, mirroring the inherent uncertainties of real warfare, is crucial for a truly immersive experience. The AI should not simply react to player actions, but also pursue its own objectives proactively, mimicking the strategic goals of a human commander.
Effective AI in Enhancing Realism, Most realistic war strategy game
Effective AI can significantly enhance the realism of a war strategy game by creating challenging and unpredictable opponents. An AI that can adapt its strategies based on player actions, effectively manage its resources, and react dynamically to changing circumstances creates a more believable and engaging war scenario. For example, an AI that successfully utilizes flanking maneuvers, anticipates player movements, and exploits weaknesses in player defenses greatly increases the sense of immersion.
Furthermore, a robust AI can allow for emergent gameplay, meaning that unexpected situations and outcomes can arise organically from the interactions between the player and the AI, further enhancing the sense of realism and unpredictability.
Balancing Realistic AI Behavior with Enjoyable Gameplay
Balancing realistic AI behavior with enjoyable gameplay presents a significant challenge for game developers. While a highly realistic AI might provide a more challenging and immersive experience, it could also lead to frustratingly difficult or unwinnable scenarios. The key lies in finding the right balance between difficulty and fairness. This can involve adjusting the AI’s aggressiveness, resourcefulness, and overall competence to create a compelling challenge without resorting to unfair tactics or exploiting game mechanics.
Careful consideration of the game’s difficulty settings and the inclusion of options for adjusting AI behavior are crucial for ensuring that the game remains both challenging and enjoyable for players of all skill levels. For example, a game might offer different AI difficulty levels, ranging from “easy” to “expert,” each with varying degrees of strategic depth and adaptive capabilities.
Historical Accuracy and Setting
The pursuit of realism in war strategy games often hinges on the accurate portrayal of historical events and settings. A game’s historical fidelity not only enhances immersion but also contributes to a deeper understanding of past conflicts and their complexities. Successfully integrating historical context adds layers of meaning and strategic depth, transforming a simple game into a compelling historical simulation.The importance of accurate representation of military units, weaponry, and tactics in a historical setting cannot be overstated.
Without this accuracy, the game risks becoming a mere fantasy, devoid of the nuances and challenges that defined real historical conflicts. This accuracy extends beyond simple aesthetics; it affects the strategic decision-making process. For example, accurately modeling the limitations of 19th-century artillery range will drastically impact battlefield positioning compared to a game featuring modern, long-range weaponry.
Impact of Historical Inaccuracies
Historical inaccuracies can significantly diminish a player’s experience and the perceived realism of a war strategy game. For instance, if a game depicts a technologically advanced unit anachronistically placed in a historical period where it did not exist, it disrupts the balance of gameplay and undermines the historical narrative. This can lead to frustration and a sense of artificiality, detracting from the immersive experience.
Similarly, inaccurate depictions of military tactics can lead to gameplay that is unrealistic and unengaging, failing to capture the strategic complexities of historical warfare. For example, representing the blitzkrieg tactics of World War II without accounting for the logistical limitations and vulnerabilities would significantly alter the strategic landscape of the game.
Visual Styles of Historically-Based War Strategy Games
Let’s compare the visual styles of three historically-based war strategy games to illustrate varying levels of detail and accuracy.First, consider a game like “Company of Heroes 2,” which features a gritty, realistic visual style. The environments are richly detailed, with accurate representations of buildings, landscapes, and military equipment. Unit models are highly detailed, reflecting the wear and tear of war, showcasing the realistic textures and damage effects.Next, imagine a game with a more stylized approach, such as “Total War: Warhammer.” While drawing inspiration from historical warfare, it utilizes a fantasy aesthetic.
The units are designed with a more fantastical look, with exaggerated features and magical elements. Environments are detailed but lean towards a more dramatic, stylized representation than photorealism.Finally, consider a game with a simpler, more abstract visual style, such as some older strategy titles. These games might use less detailed unit sprites and less realistic environments. The focus is on strategic gameplay rather than visual fidelity.
Units might be represented by simple icons, and the maps might be less detailed, sacrificing realism for ease of play and performance. The lack of detailed environments and unit models reflects a lower priority on visual representation of historical accuracy.
The Player Experience and Immersion: Most Realistic War Strategy Game
The pursuit of a truly realistic war strategy game hinges not just on historical accuracy or sophisticated AI, but on the player’s complete immersion within the game’s world. This immersion is achieved through a carefully crafted interplay of user interface, game mechanics, sound design, and visual elements, all working in concert to create a believable and engaging experience. A player who feels truly connected to their virtual army, who understands the weight of their decisions and the consequences of their actions, is a player who will be deeply invested in the game’s outcome.The user interface and game mechanics are the foundational elements of this immersive experience.
A clunky, unintuitive interface can shatter the illusion of realism, while streamlined, intuitive controls allow players to focus on strategy rather than wrestling with the game itself. Similarly, well-designed game mechanics that accurately reflect the complexities of military operations – logistics, supply chains, troop morale, unit strengths and weaknesses – are crucial for creating a sense of authenticity.
The challenge lies in striking a balance: sufficient complexity to simulate reality without overwhelming the player with unnecessary micro-management.
User Interface and Game Mechanics for Immersive Gameplay
A clean, intuitive interface is paramount. Information needs to be readily accessible without cluttering the screen. For example, a minimap that clearly displays troop positions, resource locations, and enemy movements is essential. Similarly, unit management should be streamlined, allowing players to quickly issue orders and assess the status of their forces. Real-time feedback on the impact of decisions – such as the effect of a successful flanking maneuver or the consequences of a supply line disruption – is vital for maintaining player engagement and belief in the game’s consequences.
Consider the impact of a well-designed unit upgrade system, where improvements are reflected visually and functionally, mirroring real-world technological advancements. This allows the player to feel a sense of progress and accomplishment.
The Impact of Audio and Visual Elements on Player Immersion
Sound design and music play a crucial role in shaping the atmosphere and emotional impact of the game. Realistic sounds of weaponry, troop movements, and environmental effects can significantly enhance the feeling of being present on the battlefield. Music should dynamically adjust to reflect the intensity of the situation, escalating during intense combat and calming during periods of relative peace.
Visual effects, from the realistic depiction of explosions and battlefield destruction to the detailed modeling of units and terrain, all contribute to the game’s overall believability. Imagine the impact of a meticulously rendered battlefield, complete with realistic weather effects and destructible environments, enhancing the sense of scale and consequence. The combination of realistic visuals and sounds creates a more compelling and immersive experience.
Features Contributing to High Player Engagement and Belief
Several features contribute significantly to the player’s sense of immersion and belief in the game world. These include detailed unit modeling, accurate representation of historical battles or scenarios, and a sense of consequence for player actions. A strong narrative, interwoven into the gameplay, can also help to create a more engaging and believable experience. The inclusion of realistic political and economic factors, such as resource management and diplomatic relations, further adds to the depth and complexity of the game, increasing player investment.
A system that realistically simulates the attrition of units, the effects of terrain, and the morale of troops will all enhance the sense of realism.
Elements Enhancing the Feeling of Commanding a Real Military Force
The feeling of commanding a real military force is enhanced by a number of factors.
- Realistic Unit Behavior: Units should react realistically to orders, terrain, and enemy actions, exhibiting strengths and weaknesses based on their type and equipment.
- Detailed Logistics and Supply Chains: Managing supply lines, resource allocation, and troop maintenance should be integral parts of the gameplay, reflecting the logistical challenges of real-world warfare.
- Dynamic Weather and Terrain: The impact of weather conditions and terrain on troop movements and combat effectiveness should be accurately simulated.
- Realistic Combat Modeling: Combat should be strategically challenging, requiring players to consider factors such as unit composition, terrain, and flanking maneuvers, rather than simply relying on superior numbers.
- Morale and Leadership: The morale of units should be affected by combat losses, supply shortages, and leadership decisions. The player’s actions should directly impact unit morale.
Final Wrap-Up
So, there you have it – a whirlwind tour through the fascinating world of realistic war strategy games. From the intricate mechanics that strive for historical accuracy to the often-hilarious failures of AI to outsmart us mere mortals, we’ve uncovered the key ingredients that make these games so captivating (and sometimes infuriating). Ultimately, the “most realistic” title remains subjective, dependent on individual preferences and priorities.
But one thing’s for certain: the quest for the perfect balance between realism and engaging gameplay is a battlefield all its own, and one that game developers will continue to wage for years to come. Now, if you’ll excuse me, I have a virtual army to command…and probably lose spectacularly.

